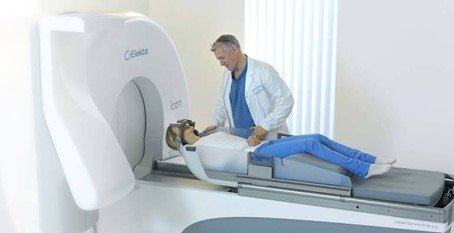
Cancer Treatment
In the human body, many regulatory mechanisms monitor and manage the pace of cell proliferation. Cancer is a result of this regulatory mechanism being compromised by genetic and environmental causes

Heart Care
Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, investigation, and treatment of disorders that affect the heart, the coronary arteries that supply it with blood, and the circulatory system. It is easier to understand the significance of the ailments that are identified and treated at the cardiology department when you consider that every cell in the body needs oxygen and nutrients, which are all transported by blood.

Urology
The diagnosis and treatment of disorders and tumors of the male and female urinary systems (the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra) as well as of the male reproductive organs is the focus of the urology clinic (the penis, testis and prostate gland).
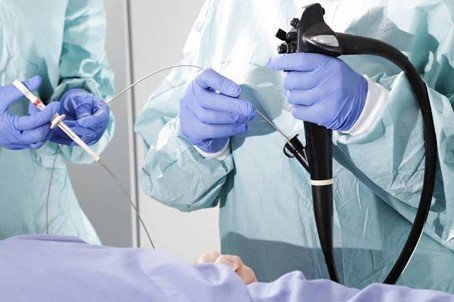
Gastroenterology
Diseases that originate in or affect the gastrointestinal system are the focus of gastroenterology, which includes disease diagnosis, examination, and medical treatment (mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, pancreas and colon). The majority of gastroenterologists conduct biopsy procedures when a malignancy is suspected in these organs.
Neurology
Disorders of the neurological system are diagnosed and treated medically through the science of neurology (brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves). Muscle and movement problems are included in the diseases that are diagnosed and treated in this field since the signals that are transmitted by the nerves are what cause muscles to function.

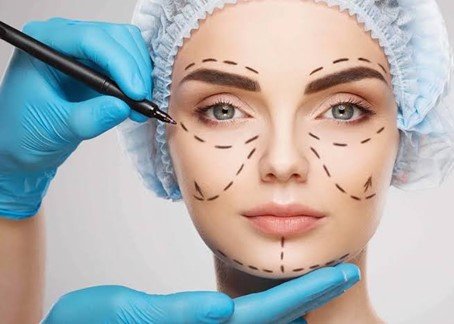
Aesthetic and Reconstructive Surgery
Mirrors need to be reconciled, and soon. Aesthetic, Plastic, and Reconstructive Surgery is a branch of medicine that focuses on the identification and treatment of inherited and acquired physical flaws, deformities, and dysfunctions. While plastic and reconstructive operations are conducted to treat diseases and restore function, aesthetic treatments are primarily performed to improve looks. All these objectives must be satisfied, except from procedures done only for cosmetic reasons.
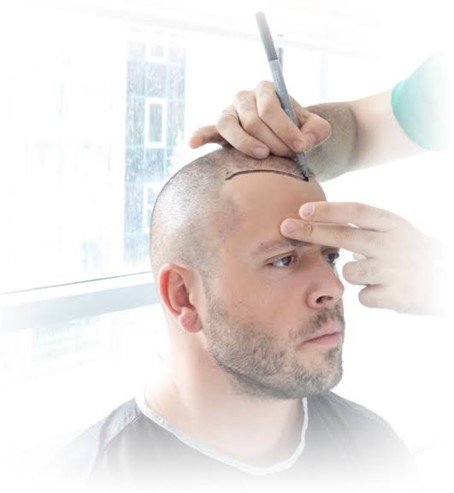
Hair Transplantation
Although there are many underlying causes of hair loss, genetic and hormonal factors are the main culprits in men and women, respectively. Today, hair loss is one of the most prevalent aesthetic issues, and hair transplantation is one of the most often carried out cosmetic surgeries. A healthy person should expect to lose between 80 and 100 hair strands per day. On the other hand, a portion of our hair (typically the hair towards the neck) is not expected to shed since they are not androgen sensitive or, to put it another way, they are not supposed to shed. For those without a hair loss disease or who do not use any medications that cause hair loss, hair transplantation is a procedure that guarantees long-term results.

IVF Treatments
The most popular treatment for infertility is in-vitro fertilization (IVF), which is one of the Assisted Reproductive Techniques. In vitro fertilization is a procedure used to create embryos that will be given to women for pregnancy by fertilizing their eggs in a lab dish with sperm from male reproductive cells. A very tiny needle is used to implant a man's sperm into an egg in cases of male factor infertility, which leads to the creation of an embryo (ICSI: Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection). The uterus of the potential mother receives these embryos in a similar manner.

Obesity Surgery
Weight Center Obesity is generally described as an excessive buildup of bodily fat. Obesity is a global pandemic that results in the accumulation of fat in arteries and around visceral organs, especially the liver. This atherosclerosis (in which plaques form inside the arteries and reduce blood flow to the tissues and organs) and subsequent health issues, such as heart disease, heart attacks, asthma, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and sleep apnea, then follow (temporary breathing lapse lasting for a few seconds during sleep).

General Surgery
There are far too many disorders to list here that the General Surgery Clinic diagnoses and treats. Despite the continued use of centuries-old surgical procedures in the field of general surgery, minimally invasive procedures including laparoscopic, endoscopic, and robot-assisted surgeries have grown in popularity as a result of technological advancements.
Bone Marrow and Stem Cell Transplantation
What is a transplant of bone marrow and stem cells? The tissue found in the spongiform tissues of bones is called bone marrow. All of the cells in the human body are derived from stem cells found in the bone marrow. Also present in the bone marrow, hematopoietic stem cells develop and differentiate into a variety of blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets). Stem cell transplantation and bone marrow transplantation have the same significance in this context.
Thoracic Surgery
For the diagnosis and treatment of the disorders listed below, the Thoracic Surgery Clinic works closely with the Radiology Unit, Laboratory, Medical Oncology, and Pulmonary Medicine clinics. Moreover, the Thoracic Surgery Clinic specifically uses the diagnostic techniques of bronchoscopy, mediastinoscopy, and videothoracoscopy.
Organ Transplantation
A diseased or wounded liver is removed and replaced with a healthy liver from a different individual, known as a donor, during a hepatic or liver transplant process.

Orthopedics and Traumatology
A medical specialty called orthopedics and traumatology treats all malignancies and diseases of the musculoskeletal system (congenital diseases, tumors, acquired diseases, trauma-related disorders).
Robotic Surgery
The notion of harming patients as little as possible when treating diseases surgically was adopted by surgery in the past. Incisions up to tens of centimeters long used to be produced during surgical procedures (for example, surgeries performed by opening the chest wall). The idea of minimally invasive surgery eventually emerged as a result of advancements in surgical instruments and methods. Because it enables surgeons to do procedures through incredibly small incisions, minimally invasive surgery attempts to reduce trauma, relieve postoperative discomfort, and shorten the length of time patients must stay in the hospital after surgery.
Spinal Cord and Spine Surgery
From the base of the head to the coccyx, the human spine has 33 vertebrae, 23 of which are movable. These 33 bones together create a column that is known as the spine or vertebral column. Between each pair of vertebrae is an intervertebral disc, which resembles a pillow. The spinal cord is located inside a canal of the spine. The cerebrospinal fluid circulates around the spinal cord in a membrane that is similar to that which surrounds the brain.

Ophtalmology
The field of ophthalmology deals with the medical and surgical diagnosis and treatment of conditions including benign and malignant tumors affecting the eyeball and the optic nerve.
Otorhinolaryngology (Ear, Nose, Throat)
Otorhinolaryngology (ENT) is a medical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the head, neck, nose, and throat in people of all ages using both medicinal and surgical methods.
Neurosurgery
The diagnosis and surgical treatment of all structural abnormalities, dysfunctions, and malignancies of the nervous system are dealt with by the neurosurgery department. Congenital anomalies, such as congenital scoliosis and kyphosis, hydrocephaly, spina bifida, meningomyelocele, and craniosynocytosis, as well as benign and malignant tumors of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations, movement disorders, and occlusions and stenosis of the ca With regard to the range of the aforementioned illnesses and disorders, the departments of neurology, neuroradiology, radiation oncology, and neurologic rehabilitation collaborate closely with the department of neurosurgery.
Gamma Knife
Gamma knife is a current treatment method that enables brain surgeons to perform surgery on abnormal areas of the brain without the need for any incision. Gamma knife is applied using a technique called stereotactic radiosurgery, and it uses gamma rays to destroy diseased brain tissue with predetermined coordinates. The system consists of 192 spherical sources, each with its own energy that does not damage normal brain tissue, and combines these sources in the diseased brain tissue to transfer very high energy to eliminate this tissue. Therefore, unlike radiation therapy, this surgical method, in which the treatment is completed in a single session, differs. It is a preferred method in situations where open brain surgery is not possible or carries a high risk. The effectiveness of gamma knife surgery depends on the sensitivity of the device used in the treatment and the methods used to detect abnormal tissue in the brain.